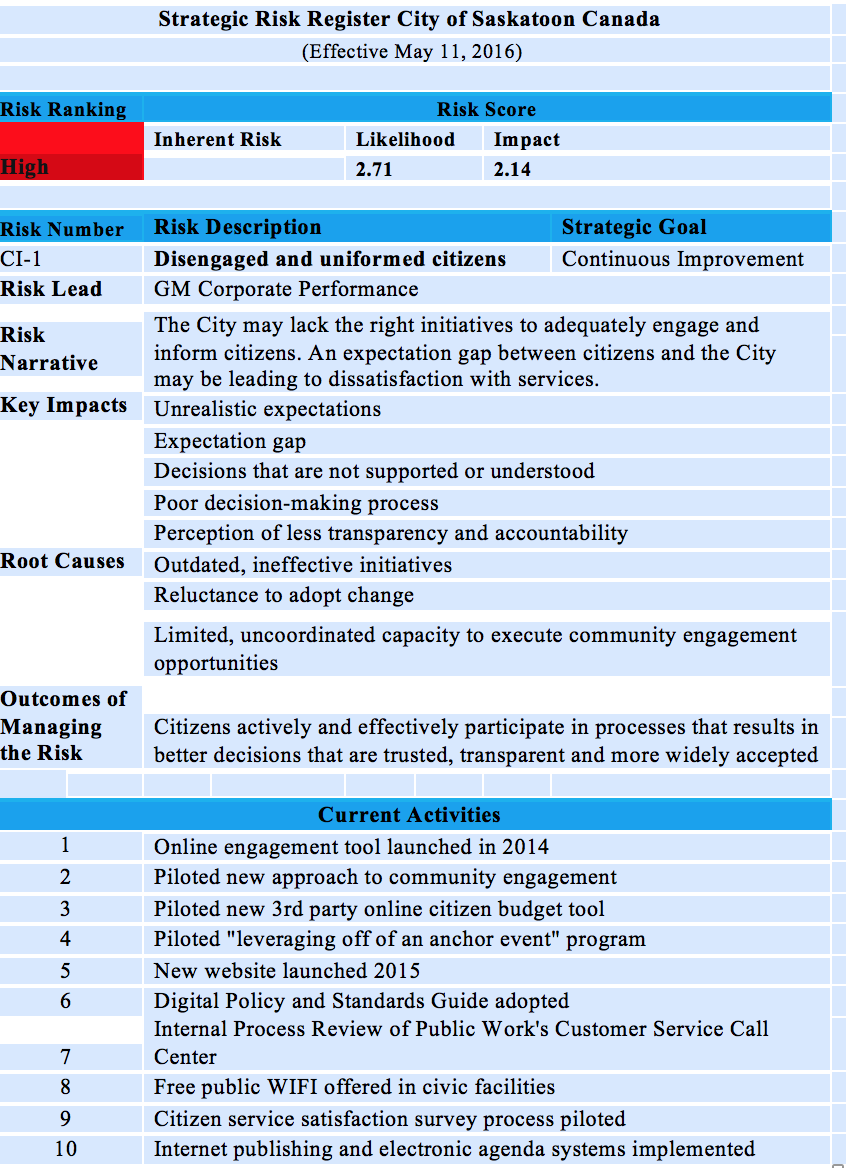
A Risk Register is a key product of the Enterprise Risk Management Methodology. The register provides information which allows them to prioritize the risk and to determine the action necessary to mitigate its impact.
This piece lists the major elements of a risk register. It also presents portions of the Strategic Risk Register for the City of Saskatoon Canada. The specific example comes from the inherent risk of Disengaged and Uninformed Citizens. Saskatoon is used because it has one of the better formats encountered so far.
Risk Register Elements
Risk Registers usually contain most of the twelve elements listed below.
- Risk category – where in your risk assessment does it get placed? In the case of Saskatoon, the risk in the strategic level.
- Risk description – what is the issue? In this case it is Disengaged and uniformed citizens
- Risk Id – How is it identified and tracked?
- Project Impact – What is the impact of the risk? For Saskatoon it is an expectation gap.
- Likelihood – What is the likelihood rating of the event? 2.71 in this case.
- Consequences – What is the impact and potential consequences? 14 and unrealistic expectations
- Risk Rank – Where in the hierarchy of the risks does it rank? In this case it ranks High.
- Risk Trigger – What are the triggers that would require implementation of a contingency plan? None specified.
- Prevention Plan – How is this risk going to be mitigated or dealt with? Action plans listed.
- Contingency Plan – What is the plan if mitigation does not work? None specified.
- Risk Owner – Who is responsible for managing and monitoring the risk? Corporate is responsible.
- Residual Risk – The amount of risk that remains after treatment has occurred. In this case the residual risk was to be determined. For space purposes it was omitted.
Saskatoon Risk Journey
Enterprise Risk Management was first proposed in 2005 in Saskatoon.. The council decided to take a bottom up approach. Thus, risks were assessed by individual departments. The Transit Department piloted the process. By 2010 the city had collated the risks and listed the top ten. At this point the program went into hiatus. In 2015 the Council revived the ERM process and updated the Key Strategic Risks. The following section from the Risk Register is a result.
Conclusion
The risk register is a key product of the ERM methodology. The register allows management to understand the risks that have been identified and indicates the was to mitigate their adverse impact. Saskatoon has one of the most comprehensive risk registers.
Bio:
James J. Kline is a Senior Member of ASQ, a Six Sigma Green Belt, a Manager of Quality/Organizational Excellence and a Certified Enterprise Risk Manager. He has over ten year’s supervisory and managerial experience in both the public and private sector. He has consulted on economic, quality and workforce development issues for state and local governments. He has authored numerous articles on quality in government and risk analysis. jeffreyk12011@live.com