 Coronavirus seems to be spreading quicker than previous pandemic potential viruses, i.e., H5N1, H7N1, SARS, Ebola, MERS, etc. Could this be the long awaited/anticipated threat realization, or is it becoming a media driven phenomenon? Needless to say, planners should be implementing some assessment analysis regarding the potential for impacting business operations. Here is a brief look back at one of my articles from 2006, entitled, “Pre-Pandemic Planning: Business Continuity Perspectives“, when Bird Flu (H5N1) was the hot topic:
Coronavirus seems to be spreading quicker than previous pandemic potential viruses, i.e., H5N1, H7N1, SARS, Ebola, MERS, etc. Could this be the long awaited/anticipated threat realization, or is it becoming a media driven phenomenon? Needless to say, planners should be implementing some assessment analysis regarding the potential for impacting business operations. Here is a brief look back at one of my articles from 2006, entitled, “Pre-Pandemic Planning: Business Continuity Perspectives“, when Bird Flu (H5N1) was the hot topic:
The business community is “not adequately prepared” for a possible avian flu pandemic, says Secretary of Health & Human Services Michael Leavitt. As of July 24, 2006, there have been 231 confirmed cases in humans resulting in 133 deaths (a mortality rate of 57%). The virus has spread to 33 countries through wild migratory birds that have now infected domestic poultry (source World Organization for Animal Health).
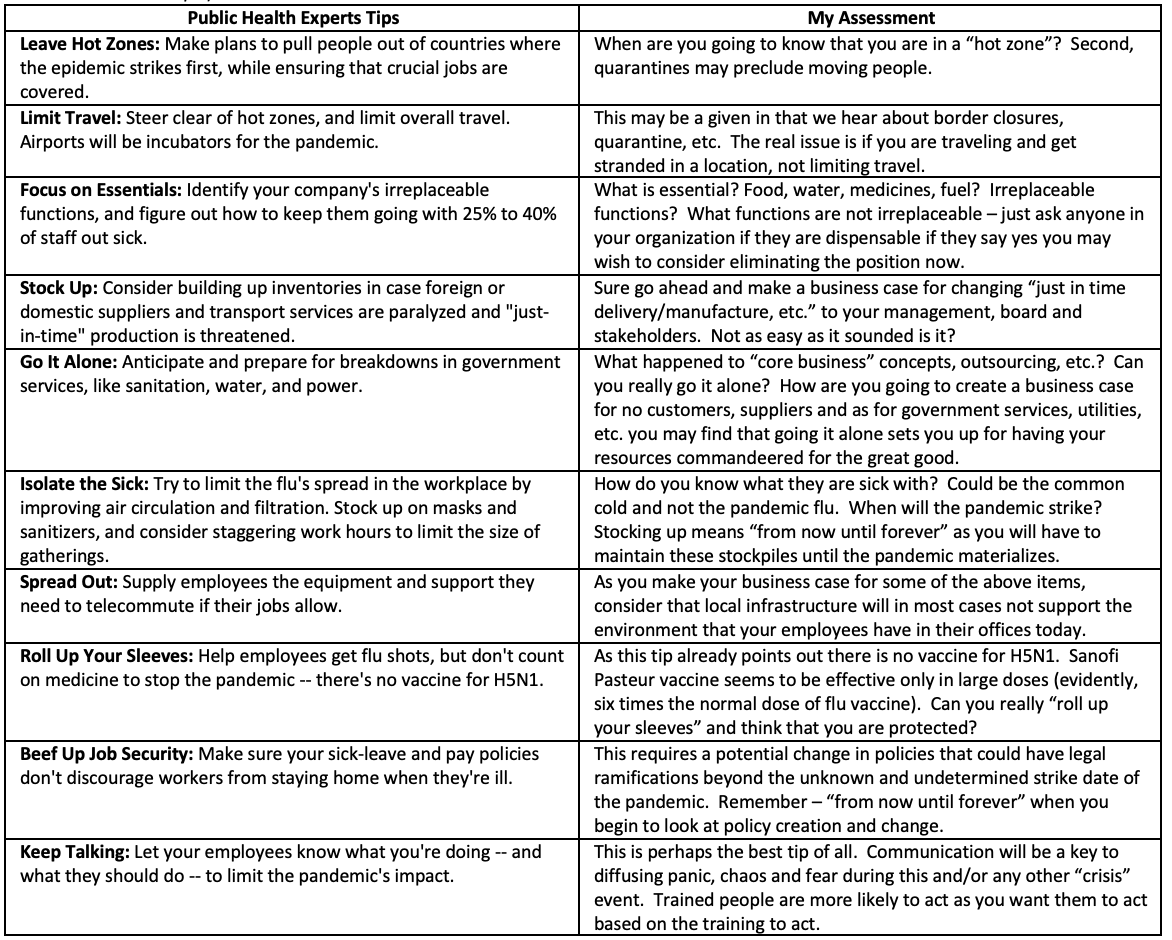
An influenza pandemic could sideline 40% of your workforce, shut down foreign trade, and degrade public services. Here are public-health experts’ tips for companies (Data: Trust for America’s Health, U.S. Health & Human Services Dept.):
Remember, the above was written in 2006, what’s changed in the last 14 years?
Coronavirus: What’s Changed since the 2006 Bird Flu Scare?
Due to the non-static nature of risk, exposures constantly change. Mitigation has the effect of altering the risk so that a new exposure is created. Mitigation buffers risk temporarily. One thing that is not taken into account when doing a risk assessment is the action of others who have the same risk exposure and are taking mitigation actions to buffer the risk exposure that they have. It is imperative to develop a mindset of constant risk monitoring and buffering activities. See my article on thinking like a commodities trader when it comes to risk.
Coronavirus, H5N1 (Bird Flu), H7N9, SARS, Ebola, etc. risk management should focus on your enterprise and its vulnerabilities – supply chain, customers, operations, etc. Leave the medial aspects to the medical profession, CDC and other better equipped entities to address the medical aspects. Your business, unless it is healthcare, should focus on basic precautions, such as, cleaning supplies that keep surfaces freer of transmission sources, education of your people in the warning signs, cough protocols (CDC has some great posters on proper way to cough). Review HR procedures, policies and practices to address the potential disruption of your workforce. Rethink work at home – it is not the same as the technology available to the office. You can also find some of my articles on the Internet that discuss pandemic planning, and, of course, my book, “Protecting Your Business in a Pandemic” available on Amazon.
SMART Planning and Preparedness
SMART is an acronym for Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, Time-Bound. When it comes to the emerging Coronavirus how do we apply SMART to our planning without becoming media driven, reactive and misfocused?
Is it Specific? Yes, it is about Coronavirus. However, should we limit our planning to such a fine point focus? Communicable diseases might be a better reference point, and, perhaps limit the liability potential for not planning for more than Coronavirus. Is it Measurable? Yes, because we can count the number of cases and track the spread via World Health Organization (WHO), Centers for Disease Control (CDC), etc. Again, I would suggest that the broader focus should be on communicable diseases; unless, of course, you can accurately predict that Coronavirus will be the one and only source of transmission. Is it Attainable? Well, we have obviously planned and prepared for pandemics before, but do we have the required knowledge to do it in this instance? Is it Relevant? From a general perspective, health issues are always relevant. However, for most non-healthcare organizations, the relevance needs to be put into the context of the operations of the organization. Of course, the protection of employees is paramount; but protecting them from what? The issue of relevance should be focused on the business operations and the potential impacts that could alter operations. These could be a lack of demand or an overwhelming demand for product/services (i.e., mask makers may not be able to keep up with demand). Is it Time-bound? Perhaps, with emergent disease, such as Coronavirus, the potential for a pandemic must be taken into account, however, the timeline is vague; until it is not.
A question for you: Is planning for the Coronavirus a S.M.A.R.T. operational or strategic objective?
Focus on Achieving Risk Parity
Risk Parity is a balancing of resources to a risk. You identify a risk and then balance the resources you allocate to buffer against the risk being realized (that is occurring). This is done for all risks that you identify and is a constant process of allocation of resources to buffer the risk based on the expectation of risk occurring and the velocity, impact and ability to sustain resilience against the risk realization. You would apply this and then constantly assess to determine what resources need to be shifted to address the risk. This can be a short-term or long-term effort. The main point is that achieving risk parity is a balancing of resources based on assessment of risk realization. Risk Parity is not static, just as risk is not static.
When I say risk is not static, I mean that when you identify a risk and take action to mitigate that risk, the risk changes with regard to your action. The risk may increase or decrease, but it changes due to the action taken. You essentially create a new form of risk that you have to assess with regard to your action to mitigate the original risk. This can become quite complex as others also will be altering the state of the risk by taking actions to buffer the risk. The network that your organization operates in reacts to actions taken to address risk (i.e., “Value Chain” – Customers, Suppliers, etc.) all are reacting and this results in a non-static risk.
A good example in the current Coronavirus situation would be the purchase of, say 10,000 masks. You have a risk that the masks will not be used; that they will be taken under “Eminent Domain” by government for the greater good of the community; that the stockpile will be insufficient for the demand, etc. These and other considerations change the risk profile (non-static). As cited above, purchasing masks creates new risks. In any event you have altered the risk and it has become non-static due to your actions and/or the actions of others within your network and external to your network. This gets us to non-aligned risk which is a risk that is influenced by nonlinear reaction.
I think that “relevance” is a very significant word relative to Key Risk Indicators (KRI’s). You can have an extensive list but if they are not relevant to the organization and its operations, they do little to enhance the risk management efforts. That said, we have to assess non-linearity and opacity with regard to the potential obfuscation of “relevance”.
Concluding Comments
For risk management and business continuity professionals Coronavirus represents fertile ground. As Coronavirus continues to spread, with each new flare-up creating a media feeding frenzy, risk management and business continuity planning will become more involved in developing plans to address this potentially “new crisis”. This created a myriad of articles and flurry of activities when Ebola arrived in the USA (Dallas, Texas, Cleveland, Ohio). The Ebola scare quickly died and with it the planning that could have been broadened to address communicable diseases.
At present, Coronavirus has too many unanswered questions. If we as, risk managers and continuity planners, claim to address risk and business continuity, shouldn’t current assessments and plans be sufficient, with minor modification, to address the issue of a pandemic? If the answer is “no, we have to create new plans”, then we have missed the point of risk management and business continuity planning. If we are actively assessing risk and have created plans that we claim are “business continuity plans”, “all hazards plans”, and plans that ensure operational resilience, then why are these plans suddenly insufficient to address the threat of a global pandemic?
As you reflect on this question look back at the generous amount of information that is still available regarding H5N1. Note that the vast majority of the articles and information were oriented toward mortality and morbidity rates. A pattern we see emerging with Coronavirus today.
Even when there is a discussion of the business impact of a pandemic flu, the orientation is focused on the response to the pandemic, a tactical approach. We need to begin to think strategically. Point of fact: we are not going to be able to stop a pandemic from occurring, whether Coronavirus, Ebola, H5N1 or some unknown emergent virus. Historically, pandemics last 500 – 800 days before burning out. Applying a first responder model to a pandemic situation that could last 500 – 800 days could be devastating. Government reactions mirror this orientation and introduce the ideas of quarantine and isolation of infected areas. There is a tendency to look at a potential pandemic in terms of its medical complications and the stresses it will place on the healthcare industry to deal with it. While the rates of illness and death associated with a pandemic are not to be taken lightly, they are not the most critically dangerous characteristics.
Three critical characteristics can be associated with a pandemic today. Speed, is the first critical characteristic. Our highly mobile society travels more frequently and at greater speed, so any pandemic will be traveling quite literally at “jet speed”. Connectivity is second critical characteristic. Supply chains, outsourcing, etc. are interdependent systems (utilities for example). We in the United States import more of our daily necessities than we produce domestically. The third critical characteristic is “economic Inertia”. Today’s business environment is the product of decades of forces acting on it and resulting in a natural “inertia”. The worldwide economy does not have to be started every day or every year, it is in motion and it stays in motion. A pandemic with a time horizon of roughly 500 – 800 days could disrupt the inertia of the global economy such that restoring it to its pre-pandemic state could be an overwhelming task due to the structure and complexity of the global economy.
The implications associated with a pandemic are admittedly both extensive and far-reaching. They are equally unpredictable, and consequently can be easily overlooked when developing strategic plans, risk assessments and business continuity plans. With today’s businesses focusing on maximizing the effectiveness of scarce resources it may appear frivolous to dedicate time to planning for an unpredictable event such as a pandemic. This logic could lead to ramifications resulting in the total failure of the enterprise. Because of the speed which a pandemic could spread globally, reaction time (i.e., reactive planning) will be almost non-existent.
About the Author
 Geary Sikich – Entrepreneur, consultant, author and business lecturer
Geary Sikich – Entrepreneur, consultant, author and business lecturer
Contact Information: E-mail: G.Sikich@att.net or gsikich@logicalmanagement.com. Telephone: 1- 219-513-6244.
Geary Sikich is a seasoned risk management professional who advises private and public sector executives to develop risk buffering strategies. With a M.Ed. in Counseling and Guidance, his focus is human capital: what people think, who they are, what they need and how they communicate. With over 30 years in management consulting as a trusted advisor, crisis manager, senior executive and educator, he brings unprecedented value to clients worldwide. Well-versed in contingency planning, risk management, human resource development, “war gaming,” as well as competitive intelligence, issues analysis, global strategy and identification of transparent vulnerabilities. He has developed more than 4,000 plans and conducted over 4,500 simulations from tabletops to full scale integrated exercises. He began his career as an officer in the U.S. Army after completing his BS in Criminology. As a thought leader, Geary leverages his skills in client attraction and the tools of LinkedIn, social media and publishing to help executives in decision analysis, strategy development and risk buffering. A well-known author, his books and articles are readily available on Amazon, Barnes & Noble and the Internet.
References
- https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2020/01/asia-chances-china-virus-meeting-looms-200122052919688.html
- https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2020/01/21/world/asia/china-coronavirus-maps.html
- https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2020/01/officials-confirm-case-coronavirus-200121192504190.html
- https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2020/01/china-confirms-human-human-transmission-coronavirus-200120162507948.html
- Sikich, Geary W., “Pre-Pandemic Planning: Business Continuity Perspectives”
- Barry, John M.; The Great Influenza, Viking Penguin, 2004, ISBN 0-670-89473-7
- Cooper, Sherry, Dr.; Don’t Fear Fear or Panic Panic, BMO Nesbitt Burns, Special Report October 11, 2005
- Drabek TE, Tamminga HL, Kilijanek TS, Adams CR. Managing multi-organizational emergency responses: emergent search and rescue networks in natural disaster and remote area settings. Natural Hazards Research and Applications Information Center. University of Colorado, Boulder CO, 1981
- Harris, Gardner, October 8, 2005 – New York Times; Bush Plan Shows U.S. Is Not Ready for Deadly Flu
- International SOS Survey Finds Only 27% of Large Organizations Have Begun to Implement Avian Flu Preparedness Plan, International SOS December 2005
- Meyer, Gerald C., “When it Hits the Fan: Managing the Nine Crises of Business,” 1986
- Mittelstadt, Michelle, Dallas Morning News, Sunday, September 11, 2005 “Four years after 9-11, Katrina reveals flaws in emergency planning”
- Mitroff, Ian, I., Avoid “E3” Thinking, Management General, 1998
- Mitroff, Ian, I., Smart Thinking for Crazy Times: The Art of Solving the Right Problems, 1998
- Sikich, Geary W., The Financial Side of Crisis, 5th Annual Seminar on Crisis Management and Risk Communication, American Petroleum Institute, 1994
- Sikich, Geary W., Managing Crisis at the Speed of Light, Disaster Recovery Journal Conference, 1999
- Sikich, Geary W., Business Continuity & Crisis Management in the Internet/E-Business Era, Teltech, 2000
- Sikich, Geary W., What is there to know about a crisis, John Liner Review, Volume 14, No. 4, 2001
- Sikich, Geary W., The World We Live in: Are You Prepared for Disaster, Crisis Communication Series, Placeware and ConferZone web-based conference series Part I, January 24, 2002
- Sikich, Geary W., September 11 Aftermath: Ten Things Your Organization Can Do Now, John Liner Review, Winter 2002, Volume 15, Number 4
- Sikich, Geary W., Graceful Degradation and Agile Restoration Synopsis, Disaster Resource Guide, 2002
- Sikich, Geary W., “Aftermath September 11th, Can Your Organization Afford to Wait”, New York State Bar Association, Federal and Commercial Litigation, Spring Conference, May 2002
- Sikich, Geary W., “Integrated Business Continuity: Maintaining Resilience in Times of Uncertainty,” PennWell Publishing, 2003
- Sikich, Geary W. “It Can’t Happen Here: All Hazards Crisis Management Planning,” PennWell Publishing 1993.
- Sikich, Geary W. and Slavik Nelson S., Industry Expectations Concerning Healthcare Response to OSHA 1910.120 “Hazardous Waste Operations and Emergency Response”; Environmental Health Manager; Spring Issue 1990, VOL. 4, No. 1.
- Sikich Geary W., “The Emergency Management Planning Handbook”, McGraw Hill, 1995.
- Sikich Geary W., Stagl, John M., “The Economic Consequences of a Pandemic”, Discover Financial Services Business Continuity Summit, 2005.
- Sikich Geary W., “A new planning paradigm: Economic Consequences of a Pandemic,” Continuity Central, 2005 (also published in Disaster Resource Guide and Continuity Forum, 2005).
- Sikich, Geary W., Stagl, John M., “Are we missing the point of pandemic planning?”; Continuity Central, December 2005.
- Sikich, Geary W., “Continuity of Leadership: Repopulating Your Chain of Command”; XBHR Newsletter, December 2005.
- Sikich, Geary W. “Economic Consequences of a Pandemic”; Emergency Corps Conference, February 2006.
- Sikich, Geary W., Stagl, John M., “Are we missing the point of pandemic planning?”; Big-Med, February 2006.
- Sikich, Geary W., “Supply Chain Continuity”; Supply & Demand Chain Executive, February 2006.
- Tainter Joseph A., “The Collapse of Complex Societies,” Cambridge University Press, 1988; Eleventh reprint 2004.
- Zuckerman, Mortimer B., New York Daily News, 20 June, 2005, “A Nightmare Scenario – H5N1 Pandemic”
- Economic Shock Waves From Avian Influenza Spreading Faster than the Disease Source: http://www.prweb.com/releases/2005/3/prweb220610.htm
 While there is merit to the above suggestions for steps that your organization can take, the concern should not be about responding to the pandemic itself (we are missing the point) the concern should be for the speed of its spread throughout the worldwide population and the economic consequences that will result as the complex global economy is shaken to its foundation. According to an International SOS survey; 91% of the respondent companies consider preparedness for Avian Flu ‘Important, Very Important or Critical’; yet only 26% have begun to implement a pandemic preparedness plan and just 1% have completed a plan, according to the survey of 200 Fortune 500 companies and other large organizations (Source International SOS).
While there is merit to the above suggestions for steps that your organization can take, the concern should not be about responding to the pandemic itself (we are missing the point) the concern should be for the speed of its spread throughout the worldwide population and the economic consequences that will result as the complex global economy is shaken to its foundation. According to an International SOS survey; 91% of the respondent companies consider preparedness for Avian Flu ‘Important, Very Important or Critical’; yet only 26% have begun to implement a pandemic preparedness plan and just 1% have completed a plan, according to the survey of 200 Fortune 500 companies and other large organizations (Source International SOS).