 The COSO ERM cube is designed as a three-dimensional box or matrix. The cube consists of 8 elements as can be seen in the above figure, specifically:
The COSO ERM cube is designed as a three-dimensional box or matrix. The cube consists of 8 elements as can be seen in the above figure, specifically:
- Internal environment. Reflects the organization’s ERM philosophy culture, risk appetite, oversight, people development, and ethical values. ‘Tone at the Top’ is often heard as a short cut reference to the state of the internal environment.
- Objective setting. Consists of strategic and tactical objectives, which provide the context for operational risk reporting and compliance. Objectives should be aligned with the enterprise risk appetite of the organization.
- Event identification. Identifies potential risks that may positively or negatively impact the organization’s ability to design and implement a risk strategy so it can meet its strategic and tactical business objectives. Positive risk is considered upside risks or opportunities. Negative risk is considered downside risk or threats or hazards to the enterprise.
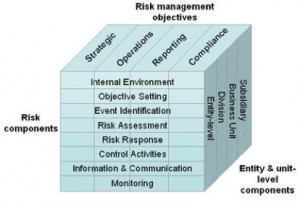
- Risk assessment. Consists of the quantitative and qualitative methods, processes, and tools to evaluate the likelihood and consequence of potential events. Common qualitative risk methods include heat maps, turtle diagrams, and FMEA. Common quantitative research methods include SPC charts, VAR analysis, and statistical distributions.
- Risk response. Consists of evaluating various risk response options and their impact on risk likelihood and consequence. Risk response is the equivalent of risk management. Items to consider in terms of an appropriate risk response can include cost-benefit analysis, evaluation of variation in cost, schedule, scope, quality; and analysis of risk against risk tolerance.
- Control activities. Consists of a system of policies, procedures, and work instructions that are integrated throughout the organization and into the supply chain. Control activities can also consist of process flow charts and project tools dealing with scope, quality, cost, and schedule variances. Control activities ensure business objectives can be met.
- Information communication. Consists of the notification and dissemination of critical information from internal and external sources so responsible parties are aware of risks and can mitigate them appropriately. Effective communication flows vertically and horizontally in the organization and into the supply chain.
- Monitoring. Consists of ongoing activities to ensure the appropriate level of risk assurance and monitoring is appropriate to the organization. If there is unusual variation within the organization, the variation is monitored and root-cause corrected so the problem variation does not recur.
The top face of the cube consists of types of objectives specifically strategic, operations, reporting, and compliance. The right face of the cube consists of entity or enterprise components, specifically entity, division, business unit, and subsidiary levels.
Lesson Learned: Notice that COSO is a similar risk management framework to ISO 31000. COSO focuses on a system of internal controls.
Bio:
Greg Hutchins PE and CERM (503.233.101 & GregH@QualityPlusEngineering.com) is the founder of:
CERMAcademy.com
800Compete.com
QualityPlusEngineering.com
WorkingIt.com
He is the evangelist behind Future of Quality: Risk®. He is currently working on the Future of Work and machine learning projects.
He is a frequent speaker and expert on Supply Chain Risk Management and cyber security. His current books available on all platform are shown below:
