 Let’s start with what is ERM? Enterprise Risk Management (ERM): is a process of planning, organizing, leading, and controlling the activities of an organization in order to minimize the effects of a risk to an organization. It expands beyond a daily run of the mill operational management! A true ERM program will have its scope expand to strategic, financial, reputational, human resource and business continuity as well as operational and legal risks. Most organizations, as they mature embark on a journey of establishing a robust Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Program!
Let’s start with what is ERM? Enterprise Risk Management (ERM): is a process of planning, organizing, leading, and controlling the activities of an organization in order to minimize the effects of a risk to an organization. It expands beyond a daily run of the mill operational management! A true ERM program will have its scope expand to strategic, financial, reputational, human resource and business continuity as well as operational and legal risks. Most organizations, as they mature embark on a journey of establishing a robust Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) Program!
As the organizations mature and processes are established, eventually the need to benchmark current processes through maturity assessment occurs. Occasionally organizations find it very useful to start their journey with the assessment as it gives them tangible goals from the beginning in reaching towards risk management leadership and excellence.
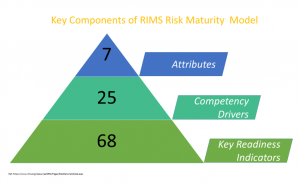 In this series, we will be looking to decode the RIMS Risk Management Model by going through each of its seven attributes one by one! We will start with the framework that is being used. The diagram below gives a visual portrait of the key components that make up the RIMS Risk Management Model.
In this series, we will be looking to decode the RIMS Risk Management Model by going through each of its seven attributes one by one! We will start with the framework that is being used. The diagram below gives a visual portrait of the key components that make up the RIMS Risk Management Model.
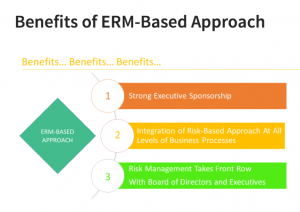
When it comes to change management or implementation of a program such as ERM, we often hear the phrase “WIFM” – What’s in it for me? Just the first attribute alone has some significant key benefits. As mentioned before it contributes towards increasing organization value. In a mature organization, the outcome or measure of ERM-based approach is seen in action through strong executive sponsorship, integration of risk-based approach in all organizational processes and by having board of directors and executive leadership selling the benefits of ERM to all business processes and demanding the ERM to take the front row in the form of frontline participation in the ERM to pay for performance, risk competency based promotions and succession planning and many other activities that will ensure that ERM is not just an annual risk mapping exercise, but, is truly how the organization thinks, behaves and lives its values.
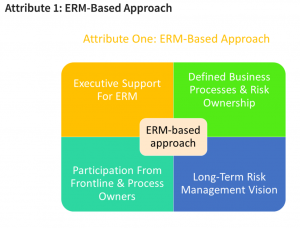 Competency #1: Executive Sponsorship For ERM
Competency #1: Executive Sponsorship For ERM
There are four key readiness indicators that allow organizations to measure their level of proficiency towards their ability to be competent in providing executive sponsorship for ERM criteria. The four key readiness indicators explore the knowledge, influence and control the Board of Directors have on operational risk priorities, organization’s ability to integrate the risk assessments into key business and project activities, linking risk management competencies with individual performance management and creating accountability at all levels of the organization.
Competency #2: Defined Business Processes & Risk Ownership
There are four key readiness indicators that allow organizations to measure their level of proficiency towards their ability to be competent in Defined Business Processes & Risk Ownership criteria. Having said that the actual RIMS Risk Maturity survey goes into Six key readiness indicators. I found the additional two are really related to the original four that are published widely. I am not sure why the actual survey has more key readiness indicators than 68 outlined in official RIMS Risk Maturity Model document. The four key readiness under this competency bench-marking assessment explore the organizational processes related to identification and assignments of risk owners, use of ERM processes, standardization of risk language between departments, business units and various levels of management, as well as communication and timeliness of risk responses.
 Competency #3: Participation From Frontline & Process Owners
Competency #3: Participation From Frontline & Process Owners
Risks are often thought to have been managed in the board rooms, however, it is often forgotten that without participation, engagement and ownership of risk mitigation strategies by frontline staff and middle management, it is not only futile but often impossible to get any traction on the ERM, strategic and operational risk management goals. The two key readiness indicators under this competency explore the clear focus and clarity of risk issues to be understood by all levels of the organization and the practices of risk assessments by all areas of the organization.
Competency #4: Long-Term Risk Management Vision
Have your ever heard the saying that “A man who does not plan long ahead will find trouble at his door.”. This is also true for ERM. They only key readiness indicator that measures the competency level for the long-term risk management vision is the organization’s ability to plan its risk management activities and scenarios that deliver long-term road map. It is also important to note that having a plan, which is not actionable is worse than not having a plan at all!
I would love to hear from others on their pet peeves about risk maturity assessment and best practices that has worked for them and their organizations. If you know of a good risk maturity model, I am interested in learning more about that too.
BIO
Jignesh is a consultant specialized in managing change involving Lean, Quality Improvement and Healthcare information technology. He has worked for Fortune 500 organizations, public sector as well as led start-ups in healthcare and biotech sector. Jignesh has developed a reputation as a dynamic, innovative, and motivational leader with over 15 years of experience as a champion of quality, safety and risk in diverse organizations. His ability to ask the right questions, and think creatively & strategically gives those he works with a “competitive advantage” in developing winning strategies for their future and the future of their organizations.
Contact: Jignesh.padia@gmail.com