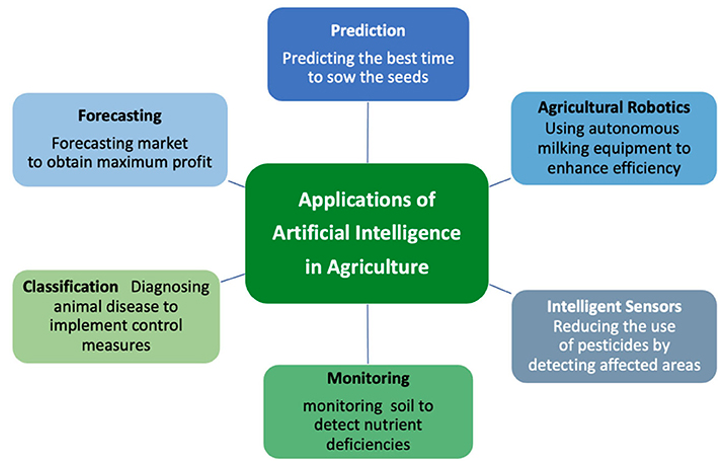
Artificial intelligence (AI) is said by many to be the most disruptive technology innovation of our lifetime. Originally a discipline limited to academic circles, AI is now commercially mainstream. Enterprises are embracing AI/machine learning (ML) and leveraging a variety of data types (structured, unstructured, and semi structured) in all lines of business (LOBs) and industries.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is said by many to be the most disruptive technology innovation of our lifetime. Originally a discipline limited to academic circles, AI is now commercially mainstream. Enterprises are embracing AI/machine learning (ML) and leveraging a variety of data types (structured, unstructured, and semi structured) in all lines of business (LOBs) and industries.
For example: Revenue growth marketing and sales teams use AI to better target prospective customers, optimize outreach campaigns, and prioritize leads. AI technologies enable social media sentiment mining, programmatic selection of advertising properties, measuring the effectiveness of marketing programs, ensuring customer loyalty, and intelligent sales recommendations.
Cost/operational efficiency: AI-powered contact center solutions accelerate time to resolution and improve the customer experience (CX). Natural language processing enables customers to speak easily about what they need without navigating through a frustrating phone tree.
Deep learning (DL) algorithms accelerate diagnosis and treatment of serious illnesses and support precision medicine.
Industrial IoT models can now predict when a machine will break down and recommend preventive maintenance, thus avoiding any potential downtime. Risk mitigation financial institutions improve loan underwriting and reduce risk. AI can also help lessen financial crime through advanced fraud detection and spotting anomalous activities.
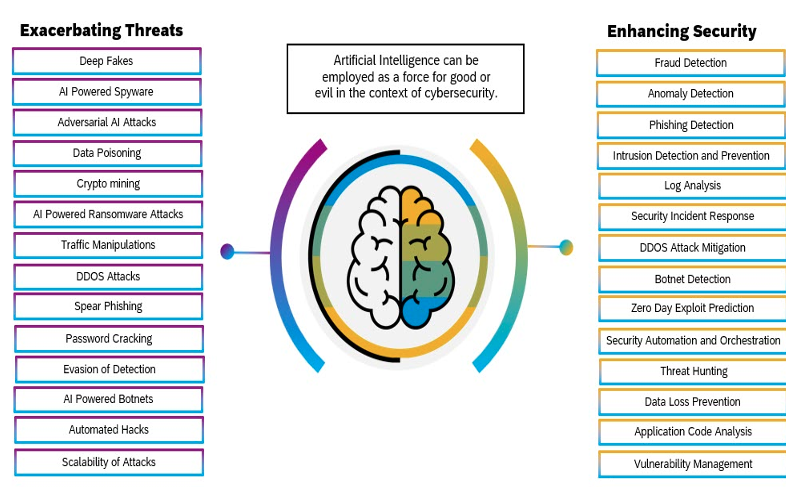
AI is playing a critical role in cybersecurity today. By improving organizations’ ability to anticipate and thwart breaches, protecting the proliferating number of threat surfaces with zero trust security frameworks, and making passwords obsolete, AI is essential to securing the perimeters of any business.
AI initiatives offer more than just cost savings. According to IDC’s AI strategies View 2021 Survey — a global survey of 2,000 organizations, with IT and LOB decision makers and influencers as respondents — AI disrupters (organizations that are repeatedly creating new business value and sustainable competitive advantage from AI) report 39% improvement in customer experience and 33% improvement in employee efficiency and accelerated innovation with the rollout of AI solutions in 2020.
This is a double-digit surge in the improvement of business outcomes compared with 2019. There is a direct correlation between AI adoption maturity and superior business outcomes. As such, there is a heightened need for enterprises to strategically scale their AI/ML initiatives.
February 2022, IDC #US48845322 Data is essential for AI/ML initiatives AI/ML requires vast volumes of data to train models Ensuring unbiased results requires diverse data sets, Models must be continuously trained with latest information to maintain predictive performance, particularly in dynamic business environments.
By taking advantage of consolidated data architecture, successful AI disrupters have been able to exploit the power of different data types and the associated ecosystem to drive innovation and transformation.
SCALING AI: INHIBITORS/CHALLENGES/NEEDS
Although many organizations understand the importance of AI and its potential impact on their business, they often struggle to move from pilot to production. As per IDC’s AI Strategies View 2021 Survey, the main challenges to implementing AI solutions include, in order of importance (see Figure 1)
- Costs (i.e., hardware accelerators and compute resource
- Lack of skilled personnel (i.e., talent)
- Lack of machine learning operations tools and technologies
- Lack of adequate volume and quality of data
- Trust and governance issue
- Technology Buyer Insight: AI/ML Implementation Challenges
Not only is data at the core of AI, it is also a key challenge. Over half of the organizations report that they lack the volumes and quality of data needed to implement an AI solution. But it’s not only a question of supply.
In the model development stage, one of the biggest challenges for businesses is getting data into the platform This can be difficult, especially if the data is not readily available in the right format.
Providing a single source of truth of governed, high-quality data is beneficial not only for data scientists but also for analysts and other data teams. To have an AI application that is relevant, accurate, and scalable, businesses need to make sure that their data, both real time or batch, is of high quality and easy to access and share securely within the organization and with the organization’s network of business partners.
To harness the full power of data with AI/ML, data scientists and machine learning engineers need the latest software frameworks and programming languages. General frameworks such as TensorFlow, MX Net, Caffe, scikit-learn, Kera’s, and Py Torch are necessary, as well as more specialized programming languages such as Python, Java, and R.
However, having the right technology is not enough. Machine learning models need the most relevant data, which may not always be inside the organization. Internal data only allows companies to see Data may be coming in real time, and so it is important to harness that data as well for real-time predictions in use cases such as fraud detection or product recommendations.
As users and use cases proliferate, machine learning–powered applications must be able to handle the extra load. If the application fails to scale, performance bottlenecks can diminish the value of using AI/ML. For example, if a customer doesn’t get the product or service recommendations they want in a timely manner, they may be less likely to come back.
Although developing a scalable system can be difficult, it is critical to do so to handle increased business demand. Failing to scale the system can lead to lost business and missed revenue opportunities. For example, delays can result in abandoned shopping carts or failure to make recommendations in a timely manner.
When scaling your system, organizations should be prepared for potential technical problems like infrastructure optimization (processing performance and elasticity), interoperability (such as supported programming languages and ML frameworks), and machine learning operations integration with existing DevOps tools and practices.
By building on top of elastic, intelligent infrastructure that requires near-zero management, organizations can more efficiently handle large volumes of data and process data without bottlenecks, regardless of number of users, in a cost-effective and time-saving way. There are several inherent benefits to this approach, including: Higher productivity.
Organizations can be more agile and creative by having a pipeline that allows for fast executions of every stage (data preparation, experimentation, model training, and deployment).
Collaboration. It is beneficial when the training and the trained model results can be leveraged by all the personas involved in the machine learning life cycle.
Cost to value optimization. It never hurts to optimize for costs and value. Scaling helps optimally utilize available resources and makes a trade-off between marginal cost and accuracy. Streamlined architecture that supports multiple.
Accelerated time to value. The pipeline should be as automated as possible so that data science professionals can focus on more complex tasks (e.g., generating value from data rather than building integrations or managing infrastructure, thereby creating a faster path to production deployments).
Effective AI requires data diversity. Similarly, the full transformative impact of AI can be realized by using a wide range of data types. Adding layers of data can improve accuracy of models and the eventual impact of applications. For example, a consumer’s basic demographic data provides a rough sketch of that person. If you add more context such as marital status, education, employment, income, and preferences like music and food choices, a more complete picture starts to form. With additional insights from recent purchases, current location, and other life events, the portrait really comes to life.
The technology buyer insight illustrated shows that while organizations are using a wide range of data types, unstructured data use is still largely untapped. In addition, data continues to be siloed (see Figure 4), making it difficult to access and govern appropriately.
Unfortunately, due to these challenges, organizations are spending more time on tasks that are not actual data science. For example, IDC’s AI Strategies View 2021 Survey found that the organizations spend the largest percentage (21%) of their total time in AI/ML life cycle in data collection/preparation.
The personas involved and surveyed include the data scientists, data architects, data engineers, machine learning engineers, application developers, and operations staff Safety Projects Data Cloud allows organizations to consolidate multiple data types and structures 14% from many sources into a single source of truth. This consolidation makes it easier for everyone involved in the AI/ML life cycle — from data preparation to model building to application deployment (see Figure 6) — to share data and collaborate effectively to derive valuable insights with speed. The sections that follow explain how organizations and personas involved in the AI/ML life cycle can benefit from using Snowflake.
Easy Access to All Relevant Data
Safety Projects International Inc. helps data scientists discover and access structured, semi structured, and unstructured data (in preview) for data science workflows, with native support for JSON, AVRO, XML, ORC, and Parquet. Even if your data is stored in an object store such as Amazon S3, Apache Glacier (in preview), and Azure Blob storage and Google Cloud Storage, you can easily query this data using External Tables. Using one set of tools for all data types shortens the data discovery and preparation cycle.
Once training data for a model is prepared, using Safety Project’s Zero-Copy Cloning feature, data scientists can take a snapshot of the data to get to a point in time view of their production data for model training reproducibility without creating redundant copies.
Customers can also use the Safety Projects tool to store and materialize features using Streams and Tasks, or their existing ELT tools such as Airflow and debt to manage transformations, partners with companies like At Scale, Rasgo, and Tecton, enabling users to adopt out-of-the-box platforms that enhance the management, discovery, and processing of features at scale through deep integrations with Safety Projects International Inc.
To provide data scientists with access to all relevant data, even that beyond their organization, the Data Cloud simplifies data sharing between partners, suppliers, vendors, and customers using Secure Data Sharing and access to third-party data through the Data Marketplace.
This offers access to unique data sets that can help increase the accuracy of models without complex data pipelines. Secure Data Sharing with Safety Projects doesn’t require data transfer via FTP or the configuration of APIs to link applications. It simplifies ETL integration and automatically synchronizes “live” data among data providers and data consumers. Because the source data is shared rather than copied, customers don’t require additional cloud storage. The Data Marketplace and Data Exchange enable data scientists to easily collaborate on models by sharing both raw and processed data.
To make model results easily accessible to the users that can act on those model results allows users to consume them via dashboards, reports, and business analytics tools by leveraging connections with ecosystem partners like Looker, Sigma, Tableau, and ThoughtSpot. With your data stored in any cloud and on any region to best suit to your needs with a consistent data experience for collaboration and migration when needed.
Flexibility of Language and Framework
By providing developers with a single platform that supports their language of choice, and popular open source and commercial solutions, Snowflake enables developers to spend more time on generating actionable business insights
Sliver is a new developer framework for Safety Projects. It allows data engineers, data scientists, and data developers to code in their familiar way with their language of choice — including Python, Scala, and Java — and execute data pipelines and ML workflows faster and more securely in a single platform. Developers want flexibility when working with data, elastically scalable environments that require near-zero administrative work and maintenance, and immediate access to the data they need. With Snowpark, developers can unlock the scale and performance of Snowflake’s engine and leverage native governance and security controls that are built into the Safety Projects platform.
 Data Robot, and H2O.ai. As per users of Amazon Sage Maker can either leverage prebuilt
Data Robot, and H2O.ai. As per users of Amazon Sage Maker can either leverage prebuilt
Performance Across the ML Workflow Steps
Safety Projects can handle large amounts of data and users simultaneously. Its intelligent, multi cluster compute infrastructure automatically scales to meet feature engineering demands without any bottlenecks or user concurrency limitations. To automate and scale feature engineering pipelines, users can leverage Streams and Tasks to have their data ready for model inference.
For bulk inference, Safety Projects simplifies the path to production with the flexibility to deploy models inside as user-defined functions (UDFs). Partners such as Dataiku, Data Robot, and H2O.ai are building a more integrated experience for users to have a guided workflow to deploy trained models effortlessly. For real-time inference, users can deploy models in an external layer (e.g., Docker) and easily request predictions directly from inside by using External Functions to communicate with the model’s API endpoint.
RECOMMENDATIONS
Today, enterprises are confronted with a complicated set of business challenges, including an increasing pace of business, an expanding volume of business data, the need to think about shared data strategies to truly derive value from data, a growing scope of global commerce, and a multitude of risks for customers, employees, and suppliers. The volume of customers and suppliers, along with regulatory complexity and multi-industry businesses, means complexity is common in global businesses.
Enterprises are rationalizing, modernizing, and transforming their enterprise application portfolios. Machine learning, natural language processing, assistive user interfaces, and advanced analytics coupled with curated data sets are advancing traditional applications to become intelligent.
These intelligent applications enable more employee insights by automating transactions that were previously stalled and bringing more data into the equation so organizations can make better decisions immediately. Organizations need a data strategy for AI, which will vary greatly depending on the size, nature, and complexity of their business and AI strategy. To accelerate innovation and time to value and enjoy a sustainable competitive advantage, technology buyers are advised to Build a talent pool of industry domain and technical experts like data engineers, data scientists, and machine learning engineers
- Get employee buy-in and trust for the data strategy with inclusivity and transparency
- Create a workflow for bringing in third-party and/or net-new data sources into the organization, including testing, buying, and seamless integration with existing internal data sets and processes
- Ensure the process is cross-functional across IT, procurement, legal, compliance, and security.
- Select a secure and governed data platform with support for all data types to support the entire AI/ML life-cycle workflow.
- Ensure flexibility in programming with support for multiple programming languages like Python, Java, and Scala, as well as leading machine learning workflows like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn
- Embrace an intelligent data grid that helps Automate and enforce universal data and usage policies across multicloud ecosystems. Automate how data is discovered, cataloged, and enriched for users Automate how to access, update, and unify data spread across distributed data and cloud landscapes without the need of doing any data movement or replication.
CONCLUSION
Many companies adopt AI as they undergo digital transformation — not just because they can, but because they must. AI is the technology helping businesses be agile, innovative, and scalable. Successful enterprises will become “AI first” organizations able to synthesize information (i.e., use AI to convert data into information and then into knowledge), learn (i.e., use AI to understand relationships between knowledge and apply learning to business problems), and deliver insights at scale (i.e., use AI to support decisions and automation). AI is becoming ubiquitous across all the functional areas of a business. IDC forecasts the overall AI software market will approach $596 billion in revenue by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 17.7%.
Data is the heart of AI initiatives. Organizations need to strengthen their data strategy for AI and adopt a secure, governed, collaborative, and scalable data platform that helps data science professionals focus on data science and scale AI initiatives seamlessly.
Bio:
Dr. Bill Pomfret of Safety Projects International Inc who has a training platform, said, “It’s important to clarify that deskless workers aren’t after any old training. Summoning teams to a white-walled room to digest endless slides no longer cuts it. Mobile learning is quickly becoming the most accessible way to get training out to those in the field or working remotely. For training to be a successful retention and recruitment tool, it needs to be an experience learner will enjoy and be in sync with today’s digital habits.”